How does the removal of federal subsidies affect investment in coastal protection infrastructure?
Abstract
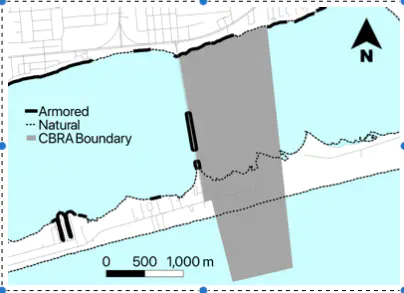
Shoreline armoring, which involves the installation of hardened structures to protect coastal property, dramatically alters shoreline composition and resulting ecological functions. Accelerating hazard threats to growing coastal communities compounds this problem, creating demand for more armoring. We examine whether designation by the U.S. Coastal Barrier Resources Act (CBRA) – enacted to disincentivize urban development on hazardous coastal barriers – is associated with lower propensities to armor shorelines. In designated areas, CBRA removes access to federally-subsidized flood insurance, infrastructure subsidies, and disaster assistance. Using logistic regression modeling, we examine armoring at the parcel scale across the State of Florida (USA), controlling for CBRA designation, land use, and local population density. Our findings reveal a significant negative relationship between CBRA designation and the odds of armoring, particularly for residential and vacant properties. As coastal areas grapple with increasing impacts from coastal hazards, removal of public subsidies may be an effective non-regulatory method for maintaining the ecological and protective benefits of natural shorelines.